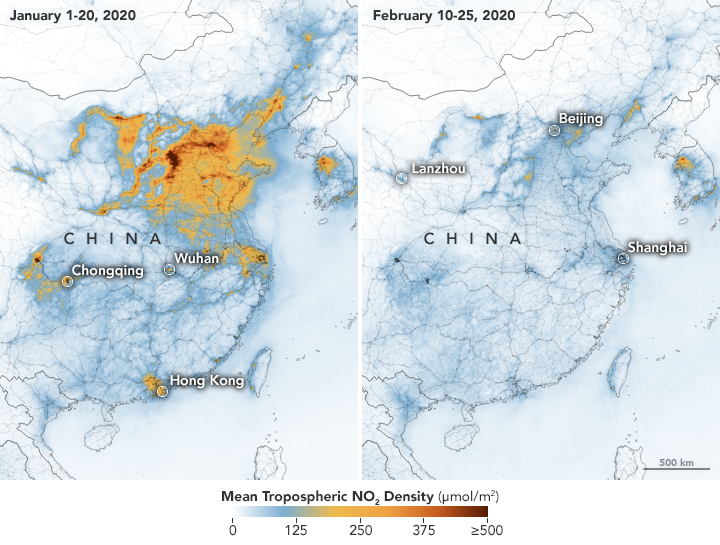
NASA and European Space Agency (ESA) pollution monitoring satellites have detected significant decreases in nitrogen dioxide (NO2) over China. There is evidence that the change is at least partly related to the economic slowdown following the outbreak of coronavirus.
At the end of 2019, medical professionals in Wuhan, China, were treating dozens of pneumonia cases that had an unknown source. Days later, researchers confirmed the illnesses were caused by a new coronavirus (COVID-19). By January 23, 2020, Chinese authorities had shut down transportation going into and out of Wuhan, as well as local businesses, in order to reduce the spread of the disease. It was the first of several quarantines set up in the country and around the world.
The maps on this page show concentrations of nitrogen dioxide, a noxious gas emitted by motor vehicles, power plants, and industrial facilities. The maps above show NO2 values across China from January 1-20, 2020 (before the quarantine) and February 10-25 (during the quarantine). The data were collected by the Tropospheric Monitoring Instrument (TROPOMI) on ESA’s Sentinel-5 satellite. A related sensor, the Ozone Monitoring Instrument (OMI) on NASA’s Aura satellite, has been making similar measurements.
“This is the first time I have seen such a dramatic drop-off over such a wide area for a specific event,” said Fei Liu, an air quality researcher at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center. Liu recalls seeing a drop in NO2 over several countries during the economic recession that began in 2008, but the decrease was gradual. Scientists also observed a significant reduction around Beijing during the 2008 Olympics, but the effect was mostly localized around that city, and pollution levels rose again once the Olympics ended.
It doesn’t take a disaster or even an emergency – beyond the one we have already created with the usual emissions levels. Reductions are possible. Disasters and loss are not mandatory, though we do make them inevitable to some extent by doing nothing. Still, these dramatic images should be instructional about what’s possible. It would be interesting to know the near-term implications of these reductions. You know, science.
