No, not the kind that continues to bottle us up in debt-ceiling kabuki. The other kind:
What was the occupiers’ one demand? They never said. And as they practiced a leaderless form of democracy, there was no one to say. The movement did have a slogan, “We Are the 99 Percent,” informed by recent economics research exposing the gap between the top 1 percent and everyone else. Yet the occupiers didn’t seem particularly inspired by the technical solutions that economists proposed. When Joseph Stiglitz, the World Bank’s former chief economist and a critic of unregulated capitalism, came to Zuccotti Park to complain about how financial markets had “misallocated capital,” he looked adorably out of place in his collared dress shirt and khakis, surrounded by activists in kaffiyehs, baseball caps, and hoodies.
Journalists trying to understand this inchoate insurgency turned for answers to Graeber, a seasoned veteran of the global justice movements of the late 1990s and early 2000s and a central figure in Zuccotti Park. It helped that he was a witty commentator with a knack for summing things up crisply. He’d been the one to suggest the language of “the 99 percent,” which he’d adapted from an article by Stiglitz. Graeber was also, as some of his fellow occupiers were surprised to learn, a major anthropological theorist. Starting as an expert on highland Madagascar, Graeber had become a free-range thinker specializing in questions of hierarchy and value but interested in virtually everything. He’d recently written a 600-page ethnography of the protests against neoliberal globalization—protests he’d joined himself.
Leaderless decision-making is the route to the real possibility, messy and littered with threat and chaos though it is. And that’s just the point – Graeber was absolutely correct about the limited political horizons [most] people come to expect. And of course we are taught this, to make nice, to play well with others, even if they actively mean us harm. And make no mistake, there are actual antagonists in our midst and we’re definitely not talking about the horn-hatted, shirtless spear holders. These are people in suits, and many of the issues that stir madness within those impatient with a complicit media or corrupt pols are seen only as rounding errors by the faceless conglomerati.
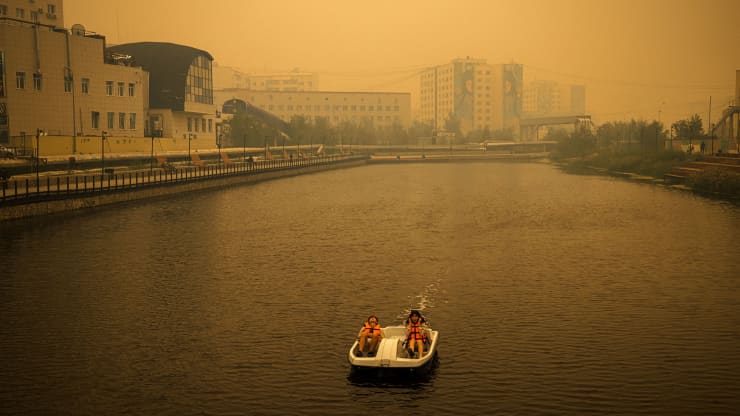
No one will be allowed – that is, given permission – to do anything about climate change, income inequality or anything else. Some call it anarchy, but being stuck with oppressive systems is a refusal to re-imagine. It’s fear – fear of messes, fear of change, fear of losing security – as if. Meanwhile, tides are lapping. Leave the grand historical narrative to Marx.